TM 5-2420-230-24-2
Lubricating Oil Contamination (007-044)
B3.9 and B5.9 Series Engines
Page 7-32
Section 7 - Lubricating Oil System - Group 07
During operation, the lubricating oil pressure will be higher
than coolant pressure. A leak in the lubricating oil cooler
will show as lubricating oil in the coolant.
However, following an engine shutdown, the residual pres-
sure in the coolant system can cause coolant to seep
through the leak path into the lubricating oil.
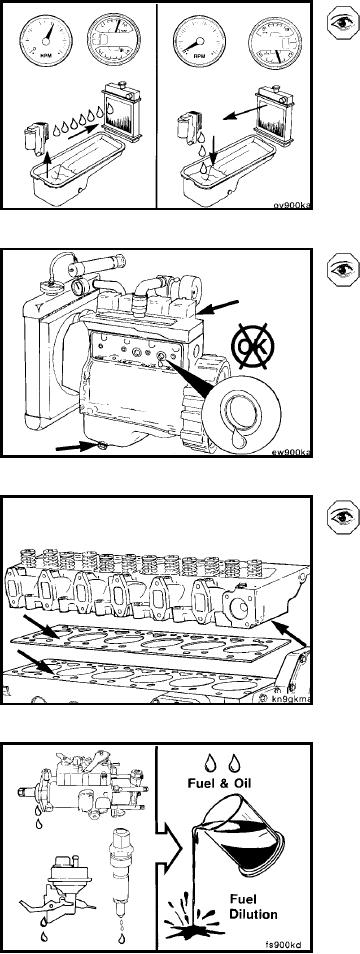
To check for leaks, pressurize the cooling system to 140
kPa [20 psi]. With the system pressurized, remove the
following components, and inspect for leaks.
Valve covers (leaks indicate cracked head)
Lubricating oil drain plug (leaks indicate defective
lubricating oil cooler, head gasket, cracked head or
block)
Tappet cover (expansion plug leak).
Coolant in the lubricating oil can be caused by a damaged
cylinder head gasket or cracked cylinder head or block.
Remove the cylinder head and gasket, and inspect for
cracks or damage.
Fuel-Diluted Lubricating Oil
Fuel dilution is limited to five sources:
1. Injection pump shaft seal
2. Fuel leaking by the rings
3. Fuel transfer pump
4. A crack in the cylinder head from the fuel filter location
to the air intake
5. Injector leakage.
L-1044

